Clifford Ellis (1907-1985)
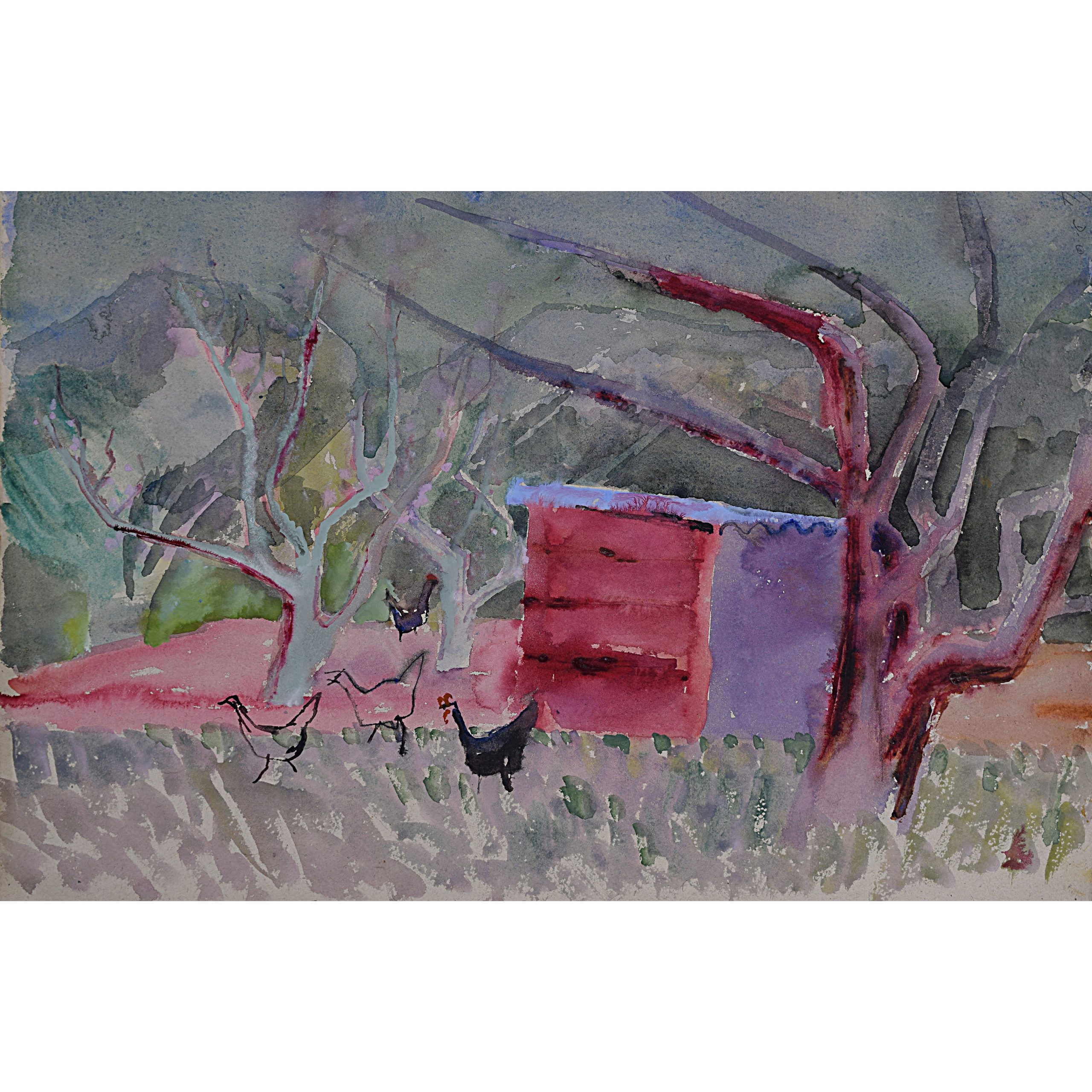
Hens by a chicken shed at Corsham Court
Watercolour
37x56cm
Provenance: the family of the artist, by descent.
Here Ellis paints the hens at Corsham Court together with their chicken shed.
Born in Bognor in Sussex and trained at St Martin’s School of Art and Regent Street Polytechnic, Ellis was a graphic artist and illustrator who is best known for the posters he produced for London Transport during the 1930s. He generally collaborated with his wife Rosemary – whom he married in 1931 – on their posters. The General Post Office, Shell, and The Empire Marketing Board were also clients for their posters. They signed their posters C&RE, their initials being in alphabetical order and they are readily recognisable by their ebullient use of colour and form.
Employed during the war as a camoufleur, along with so many other artists, Clifford was also an official war artist, serving with the Grenadier Guards. Rosemary, meanwhile, was an artist for the Recording Britain project.
Following the war they trained art teachers at Bath Academy of Art. They also designed a series of nearly one hundred book jackets for Collins New Naturalist series, published between 1945 and 1982.
Clifford Ellis studied illustration at the Regent Street Polytechnic, an institution that specialised in ’practical trade classes’, from 1924-27. He went on to design book covers (notably for Collins’ ‘New Naturalist’ series) and posters for London Transport, the General Post Office, Shell-Mex, the Empire Marketing Board and J. Lyons & Co., along with his wife, Rosemary Ellis, whom he married in 1931 while he was teaching at the Polytechnic.
The couple’s poster designs combine striking colour with bold typography and depict stylised scenes of the countryside, birds and animals. In the 1930s London Transport commissioned over forty posters a year from well-known artists such as Laura Knight, CRW Nevinson, Edward Wadsworth, Eric Ravilious, Paul Nash, Graham Sutherland and Edward McKnight Kauffer – a bold policy that did much to popularise avant-garde artistic styles that stemmed from Cubism, Futurism and Abstraction. Such an influence is clear in the Ellises poster ‘It’s better to shop early’ (above, 1935) in which arms, hands and parcels are disjointed and angular with the text on a slant, like the collaged newsprint insertions of synthetic Cubism.
This strong foundation in graphic art clearly influenced his approach to composition for the rest of his career. Even his later abstract work, though tonally subtle, is based on a simple but powerful linear design. ‘The Coming of the Ice Age’, a series of watercolour and crayon studies (one large finished canvas, ‘Advance of an Ice Age’, exists in the collection of Derbyshire and Derby School Library Services) reduces natural forms to simplified shapes and colour planes, though retaining the texture of brushstrokes and crayon. The Ellises visited the Devon coastal town of Teignmouth to carry out a commission for Lyons for a lithograph in 1947, and the rocky bay with its whitewashed buildings and sailboats (below) caught Clifford’s imagination. He painted numerous preparatory watercolour views for the lithograph, while both the grey-blue colour palette as well as the pleasing repetitive geometry of sails reflected on water might be discerned in later abstract works.
During the Second World War Ellis served as a camouflage artist and official war artist with the Grenadier Guards. Roland Penrose was another British artist who worked in this area and wrote ‘The Home Guard Manual of Camouflage’ which effectively adapted modern painting techniques for use in warfare. The tonal colour range of many of Ellis’s post-war paintings and the abstract network of shapes – for instance the pale blue patchwork ‘glacier’ in the ‘Coming of the Ice Age III’ (below) – seem to hark back to the art of the modernist camoufleur.
Ellis played another important role during the war, painting and drawing scenes of Bath for the Recording Britain project. This project was conceived by Kenneth Clark, then Director of the National Gallery, alongside the official War Artists scheme; its aim was to document Britain’s landscape and architectural heritage in the face of the imminent threat of invasion and bomb damage. It also had a propaganda motive; the resulting works were exhibited during the war and aimed to boost the nation’s morale (they are now in the collection of the V&A). The paintings were predominantly in watercolour, a traditional British medium that Clark was keen to promote and felt would complement the subject matter. Two of Ellis’ pupils, discussing his watercolour sketch of VE Day in Bath, recall him as quietly observant but also someone who enjoyed life; the painting is spontaneous and full of the movement of dancing figures and waving flags.
In particular, Ellis was commissioned to depict examples of Bath’s decorative architectural ironwork before it was removed to help the war effort and he also recorded the effects of bombing raids on the city.
Meanwhile Ellis had joined the staff of the Bath School of Art (or Bath Technical College). Its temporary residence was destroyed by bombs in 1942 and Walter Sickert’s house at Bathampton offered as a refuge (Sickert, who had taught at the School, died in January 1942). After the war the School began its transformation into the Bath Academy of Art based at Corsham Court, of which Ellis was the Head from 1937-72, training art teachers and developing a pioneering new syllabus.
If you are interested email info@manningfineart.co.uk or call us on 07929 749056.
Condition: Excellent. In a conservation mount.