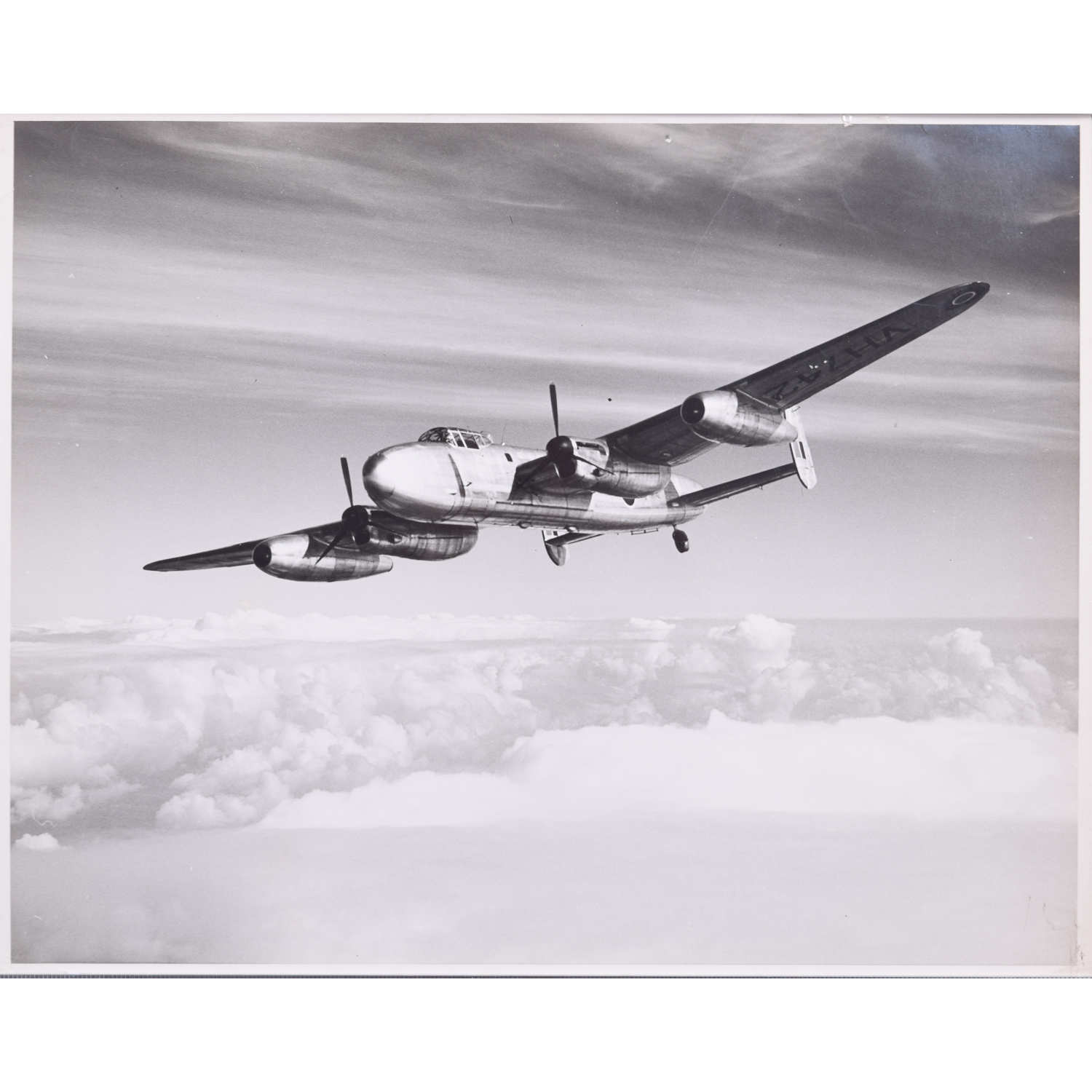
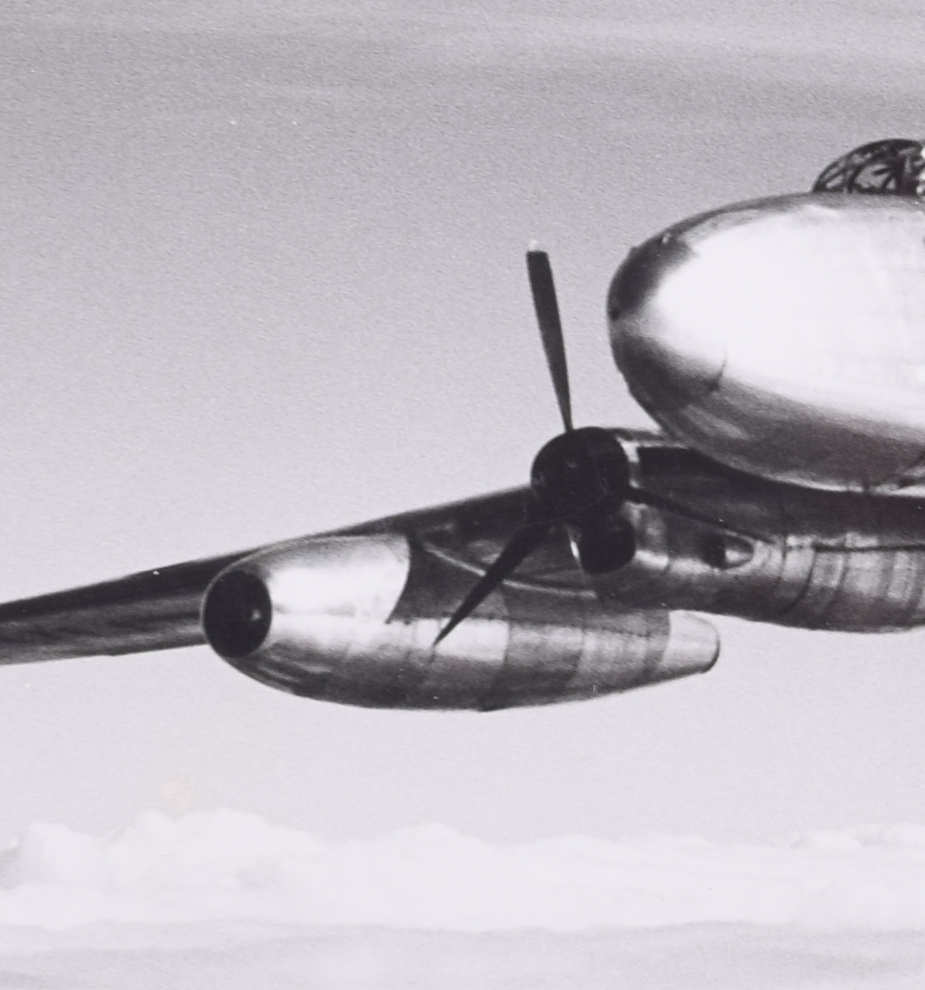
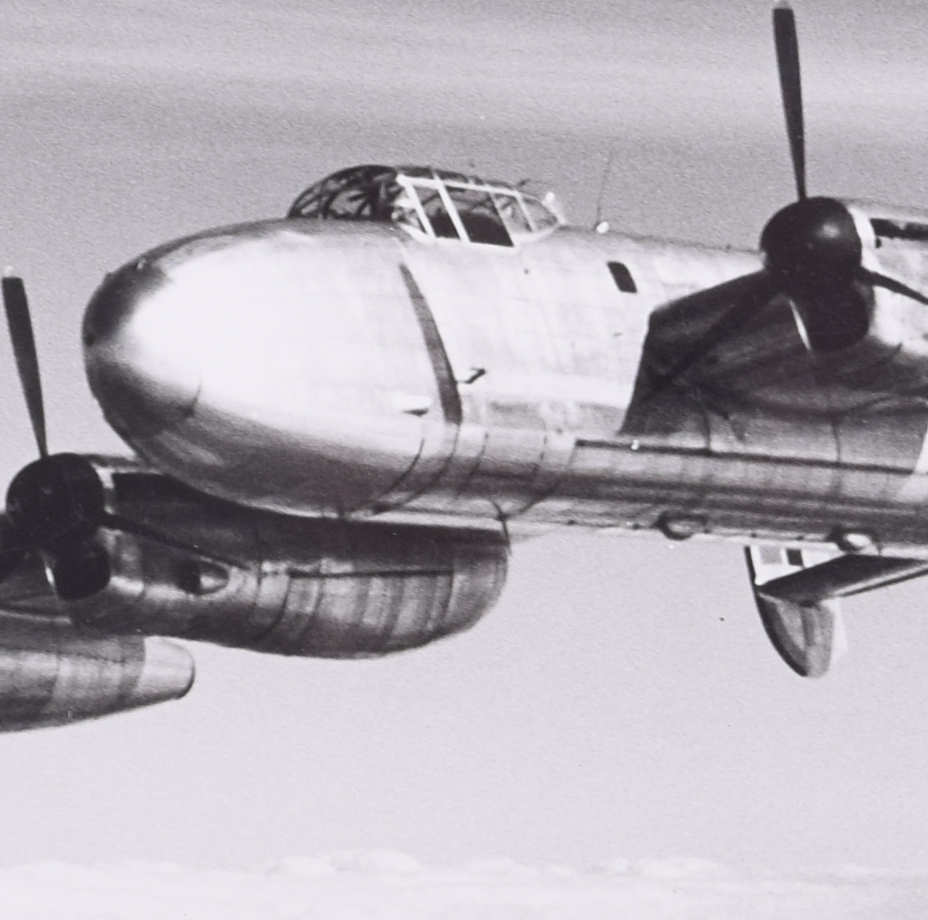
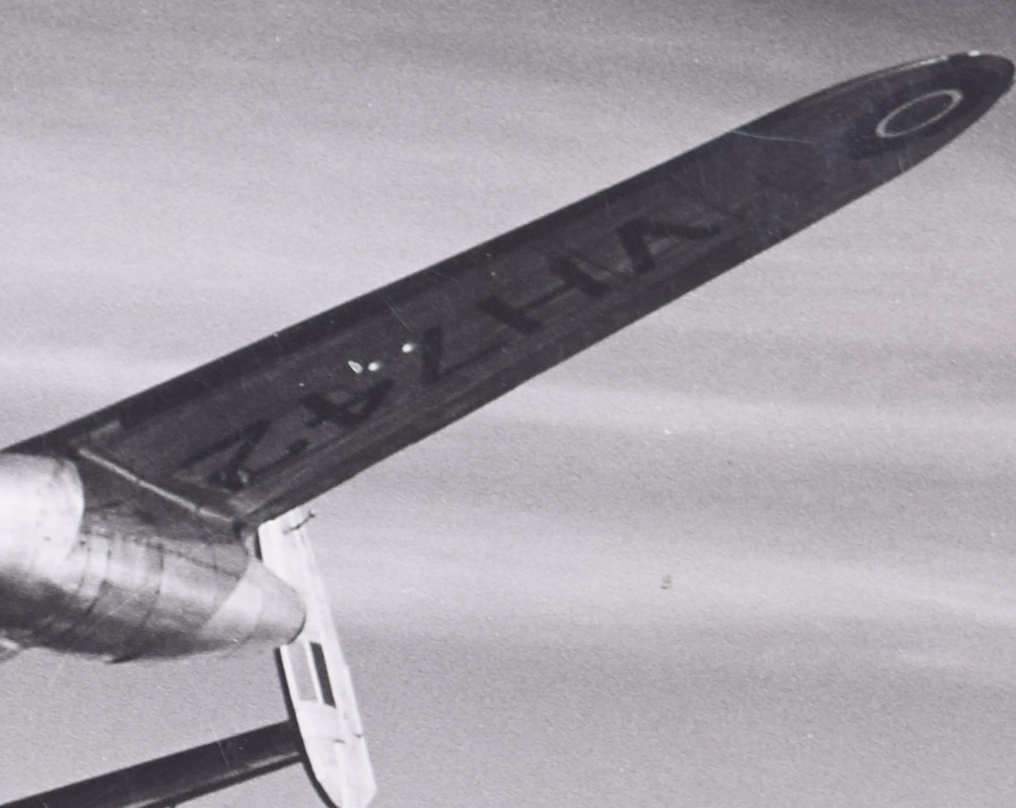
Charles E Brown (1896-1982)
Lancastrian VH742 – The first Jet Airliner
Original Silver Gelatin photograph, 1940s
19 x 24 cm
Stamped to reverse ‘Charles E Brown’ with address and 6140-2 reference number, together with press release reading:
“THE FIRST JET LINER
“Captain R T Shepherd, Rolls Royce chief test pilot, demonstrating the remarkable performance of the 62,500 lb Avro LANCASTRIAN on the two NENE jets alone. With the two Merlins and their propellors stopped one is struck by the entire absence of visible moving parts. Even more noticeable is the reduced noise and complete lack of vibration.”
The Lancastrian was developed from the Lancaster bomber with armaments and armour removed, and a new – streamlined – nose. The first batch were made by converting Lancaster bombers, latter batches made from scratch. The Lancaster had been designed to carry bombs rather than passengers, and so the space available meant that whilst the Lancastrian was not suitable for large numbers of passengers it was admirably suited to carrying mail and other perishable goods.
First to fly was Lancastrian VH742, delivered to the Rolls-Royce flight development airfield at Hucknall in October 1945. Its outer Merlin engines were removed and the nacelles were also taken away, while the fuel system was completely rebuilt to carry both gasoline for the inner engines and kerosine for the new jets. In the outer positions were added completely new nacelles housing Nene turbojets, then the most powerful jet engines in the world. It flew again on August 14, 1946 with two Merlins and two Nenes.
On September 19, 1946 this aircraft acted as the world’s first jet airliner by making three passenger flights carrying representatives of the Press as well as Ministry officials and other passengers (who were all most impressed and suggested that an airline that could offer jet travel would be the talk of the world). Rolls-Royce also flew a second Nene-Lancastrian, VH737, and two Avon-Lancastrians, VM732 and VL970. The latter The first flight of a jet airliner was reported as follows:
“The Nene-Lanc, Flies to Paris
“THE flight of the Nene Lancaster from London to Paris last Monday, to play its part in connection with the exhibition, may be said to have marked a historic part in British aircraft development, for it constituted the first time that any jet-powered airliner had flown from one country to another. Moreover, since this particular aircraft has been flying fairly regularly since round about the time of the Radlett exhibition, the flight to Paris was no special performance, but merely one more public demonstration of its inherent reliability.
“In the hands of Capt. R. T. Shepherd, chief test pilot for Rolls-Royce, the “Nene-Lanc” landed at Le Bourget at 10.58 a.m., G.M.T., after a 50-minute flight from London Airport, giving an average speed of 247.5 m.p.h. [398.3 kilometers per hour] Two passengers were carried in addition to the crew; they were Mr. Roy Chadwick, the Avro designer, and Mr. R. B. William Thompson, Chief Information Officer of the Ministry of Supply.
“Capt. Shepherd said that he was very pleased with the aircraft’s performance and added that, but for having to circle Le Bourget Airport Twice before landing, the flight would have been completed in 43 minutes.”
FLIGHT and AIRCRAFT ENGINEER, No. 1978. Vol. L., Thursday, November 21st, 1946 at Page 561, Column 2.
Charles E Brown was a famous photographer of aircraft whose father was a butcher in Wimbledon, London. Young Charles was given a camera for his 14th birthday and in 1911 photographed an Edwardian gentleman in trouble landing his balloon in neighbouring Southfields. This photograph was published in the Daily Mirror – the fee being half a crown – and Brown was encouraged to join the Daily Mirror’s photography department upon leaving school at 16.
Towards the end of the First World War he served with the Royal Air Force at their official London Photographic Centre. Following the war, he took to photographing trains, and captured a famous photograph of a Southern Railway locomotive that was used for the following ten years in railway posters. The income from this allowed him to pursue his passion of aviation photography in the 1920s and 1930s, from which commissions from the Air Ministry and Fleet Air Arm followed. During the war his work included commissions for Aeronautics magazine.
Provenance: from the collection of Philip J R Moyes, author of many books on the RAF, most notably The Pictorial History which ran to several volumes.
Condition: Generally very good.